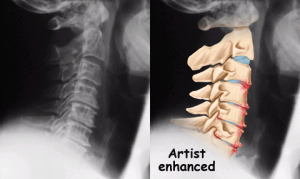
SCOLIOSIS is a spinal abnormality in normal condition straight transformed into the form of the letter “S”.
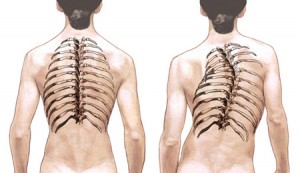
Generally the patient is never aware of this disorder and he only realized after notified by the family or close relatives who accidentally see any difference. Some are only realized after his massage notified by builders who felt an unusual lump on his client’s body.
The presence of scoliosis will certainly have an impact on health is concerned which can start with the lightest such as pain, muscle pain, nerve pain, respiratory disruption, psychological disorders and even difficulty working because of limited motion in the cause.
Causes of Scoliosis
When viewed from the top 85% of the scoliosis is unknown or known as idiopathic, while the rest may be due to causes such as congenital disorders / birth defects, nervous system disorders, connective tissue, or other causes.
Asymmetric limb growth also widely referred to as the cause of scoliosis is why scoliosis is also known as structural or nonstructural abnormalities. The presence of factor descendants also quite large which is found in some cases of scoliosis in the family members
Diagnosis of Scoliosis
To detect or diagnose the presence of scoliosis do a physical examination by a physician experienced in handling cases of scoliosis and also in conjunction with radiological examinations done / X-ray.
With radiological examination the form of scoliosis that occurs can be easily identified. In addition it is also important to know besasrnya Cobb angle formed by the scoliosis condition. The angles formed by the arms of the spine will determine what kind of medical procedures undergone by the patient yangharus.
From the research that is then said to be formed when the Cobb angle less than 10 degrees then the least that should be done regularly so that regular observations can be minimized due to the possible. How to consult a physician who has handled before and radiology re-examination.
When the angle is between 10 to less than 40 degrees then the corresponding need of yangbersifat nonoperatif, but if the angle is more than 40 degrees, the patient requires assistance from a specialist orthopedic surgery fatherly / correction.
Another advantage of radiology examinations are pelvic examination can be done in order to set the level of development or fusion of the bone itself. When visible bone fusion is still not / do not merge the possibility of scoliosis patients worse becomes larger and also the opposite situation.
Sometimes patients feel reluctant to perform radiology examinations by various reasons and asked the doctor to do the examination at the next opportunity, or even at the end of treatment. For physician examination absolutely must be done so that he / doctor and the patient’s family can know the state of scoliosis in the early treatment of disease and the results of such an examination is very valuable because it will be used to compare the results of treatment with the initial state before handling the case.
Treatment For Scoliosis
Treatment or Management for Scoliosis doesn’t mean it will give the results of of a normal bone like 100% straight. This is considering that the bone is growing so that when it is found at an earlier age would provide a much better result than in adulthood.
Thus the aim of the treatment of the stretcher over to prevent damage to other organs caused by the occurrence of scoliosis. That means we still have to find the cause of scoliosis itself and wherever possible resolved that the disease does not progress to worse.
To handle as mentioned above may be operative and non-operative according to the lightness or severeness of scoliosis. For handling nonoperatif is currently offered so many advertisements that claim to cure scoliosis, but is actually just a medically recognized is the use of brace or support that serves as a buffer from the bone which is not straight. Scoliosis brace used on the course not the same as that used by fellow dentists to repair teeth arrangement because there scoliosis soft tissue such as skin is not as hard as the teeth and will also cause pain overemphasis pad. Brace therefore can not simply be bought, but must go through the patient’s condition. In addition, patients should also be disciplined in using it and most of his active life he had to use the brace. Constraints faced by patients at the time of use is a feeling of tightness, heaviness, heat and sometimes itchy sometimes causing patients not disciplined in use resulting in the ineffectiveness of the brace that ultimately can not deliver results as expected with.
Sports Therapy and Scoliosis
When patients experience difficulties in using the brace then do sports therapy is one way that can be used considering sports therapy is a treatment program that uses sports to measurably improve the health of a person or help cure certain diseases such as scoliosis. The use of sports therapy together is also a combination that can be done to improve the effectiveness of the undertaken treatment.
In cases of scoliosis will be an imbalance of working muscles in the spine to change shape and vice versa where the muscles that make the spine is tilted to one side. Thus we can give you a workout that will making working these muscles become more balanced and also resulted in a more straight spine, consequently the body becomes more relaxed and comfortable of course.
Exercises are performed will become more efficiently by using the computer equipment is referred to as EMG / Electrical MyoGraphy. In the presence of such a device would be seen as what types of exercises recruit the most muscle fibers during a workout which would impact on the acceleration of the results to be obtained by the patient concerned.
What also needs to be known is as therapy theray other sports do not make changes directly to the bone changes shape so that the repair is more temporary, which is why patients should continue to diligently perform the exercise has been known to be sustainable. It is equivalent to the brace that would otherwise be used again megembalikan original slant to forms bone. Therefore, when not practicing sports therapy regularly then auto-muscles are also no longer able to repair the abnormal bone structure.
This does not mean patients should absolutely continue to practice in sports therapy but just do exercises at home megingat he has been able to do it yourself, and after that to monitoring of the results of the exercise can be consulted on the treating physician. For sufferers \ scoliosis also be counting on weight because weight loss. Excessive especially for those who suffer from obesity will further aggravate the situation of his / her scoliosis.
Conclusion of Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a disorder that occurs in the spine that cause is still unclear, but if the cause is already made it known that the condition usually can also be resolved. In handling can besifat operative and nonoperatif. For those who nonoperatif overcome scoliosis with sports therapy is the best option because it is active in training the muscles are weak and can be combined with other nonoperatif treatment.
The result is although it will not be a normal people with scoliosis are forever, but at least it can reduce the negative impact caused by scoliosis and therefore the patient must always do exercise sports therapy alone and do some control to the doctor regularly.
Need Consultation? Please contact us by +65 6471 2691.