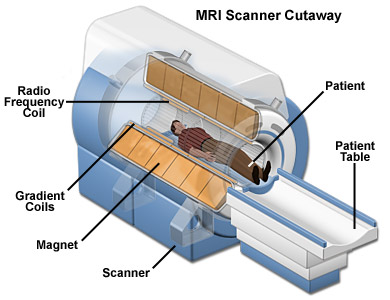
 What is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)?
What is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures. MRI makes use of the property of Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to image nuclei of atoms inside the body.
How to Prepare for MRI Examination?
As the strong magnetic field used for MRI will pull on any ferrogmagnetic metal object implanted in the body, it is important that all metallic items including magnetic strips (e.g., in bank or credit cards) be removed before entering the scanning room. The presence of metal will also degrade the MRI image and therefore has to be removed in order to optimise your examination.
In most cases surgical staples, plates, pins and screw s pose no risk during MRI if they have been in place for more than four to six weeks.
If there is a doubt, an x-ray may be required to verify the presence of any metal in your body or head.
You are discouraged to apply make-up or sprays on your body or hair as these may contain metallic dust and affect the images.
You will be asked to fill in a pre-examination questionnaire to ensure that no significant medical history is forgotten and the staff is fully aware of any metal that may be in your body.
Unless a contrast injection is required, you may eat normally and go about your daily routine. Continue to take any medication prescribed by your doctor unless otherwise directed.
If you are claustrophobic, sedation may be required. Please highlight this when making an appointment and further instructions will be given.
On the day of Examination
Before the Examination, you will need to:
- Fill in a questionnaire on your medical history.
- Remove items like your wallet, watch, keys and magnetic strip cards (eg ATM, credit cards). Lockers are provided.
- Change to a gown to prevent metallic objects from being attracted by the powerful magnet.
During the MRI
- You will be positioned on a padded table and slowly moved into an open magnet that surrounds the body with a magnetic field.
- Once you are comfortably positioned, it is important that you remain relaxed and completely still during the scan. Movement will result in unclear images.
- There will be a faint knocking, intermittent humming and thumping sounds. These represent changes in the magnetic field. Earplugs will be provided.
- Breathe normally, as there is nothing about the procedure to make you uncomfortable or painful. You may notice a warm feeling in the area under examination; this is normal but if it bothers you please let us know.
- In some cases, the doctor may order an image enhancement agent. This is a fluid which is injected into a vein probably in your arm. If this is required, it does not mean that your condition is more serious. So do not be concerned.
- You will have voice contact with the radiographer at all times and you can be seen clearly from the control room.
How long will it take?
Depending on the information your doctor needs, the examination can take between 30 to 45 minutes.
How Safe is MRI?
MRI is quite safe in the majority of patients. Certain patients may not be able to have an MRI. These include people who get nervous in small spaces (claustrophobic) and those with implanted medical devices such as aneurysm clips in the brain, heart pacemakers and cochlear (inner ear) implants. Also, people with pieces of metal close to or in an important organ (such as the eye) may not be scanned. There are a few additional safety considerations and some exceptions based on individual circumstances.
Also, certain metal objects that we common have on our persons like watches, credit cards, hair pins, writing pens, etc. may be damaged by the MRI scanner or may be pulled away from our bodies if we go into an MRI room. Also, metal can sometimes cause poor pictures if it is close to the part being scanned. For these reasons, patients are asked to remove these objects before entering the MRI scanner.
What will I Experience During MRI Examination?
You will most likely be lying on a special table that moves into the center of the magnet. Prior to going into the magnet you will be offered earplugs to reduce the noise that you hear. You will then hear some “hammering” noises while the scanner is preparing for scanning and taking the pictures. During this hammering noise, it is important not to move, as this would blur the pictures. You may also feel some vibration during the hammering noise and some slight movement of the table during the examination. Some patients will be given an injection in their arm of a substance that improves certain types of pictures. This substance, called a “contrast agent”, is very safe and is unrelated to the iodine used for CAT scans and kidney x-rays.
What are the Uses and Advantages of a MRI Scan Other Types of Scans?
MRI scanners are good at looking at the non-bony parts or “soft tissues” of the body. In particular, the brain, spinal cord and nerves are seen much more clearly with MRI than with regular x-rays and CAT scans. Also, muscles, ligaments and tendons are seen quite well so that MRI scans are commonly used to look at knees and shoulders following injuries. A MRI scanner uses no x-rays or other radiation. A disadvantage of MRI is it’s higher cost compared to a regular x-ray or CAT scan. Also, CAT scans are frequently better at looking at the bones that MRI.
What are the Benefits and Risks?
Benefits:
- Images of the soft-tissue structures of the body such as meniscus, anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), lumbar discs and ligaments are clearer and more detailed than with other imaging methods.
- MRI can help physicians evaluate the function as well as the structure of many organs.
- The detail makes MRI an invaluable tool in early diagnosis and evaluation of tumours.
- MRI contrast material is less likely to produce an allergic reaction that the iodine-based materials used for conventional investigation.
- MRI enables the detection of abnormalities that might be obscured by bone with other imaging methods.
- MRI provides a fast, non-invasive alternative to x-ray angiography for diagnosis problems of the knee and spine system.
- Exposure to radiation is avoided.
Risks:
- An undetected metal implant may be affected by the strong magnetic field.
- MRI is generally avoided in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. Doctors usually use other methods of imaging such as ultrasound, on pregnant women unless there is a strong medical reason to use MRI.
When you can expect the Result?
The MRI radiologist and radiographer will review the images during the scan to check that they are clear. The report will be sent to the orthopaedic doctor, Dr. Kevin Yip who will then discuss the scan results with you.
Need consultation? Our professional orthopaedic specialist, Dr. Kevin Yip, has more than 20 years experience. Be assured that you will be receiving professional treatments that suit your needs.
Call +65 6471 2675
